TCP IP model can also be used as an exchange protocol in private PC organizations (intranet or extranet).
The entire Internet convention suite (many guidelines and techniques) is often called TCP / IP. TCP and IP are two essential programs, but there are many programs to review in this suite. The TCP / IP presentation suite exists as a reflective layer between the web application and the orientation/transaction interface.
The TCP IP model determines the data exchange preparation method on the system by comparing connections from beginning to end. The comparison relationship identifies how to deteriorate, compose, spread, guide and reach the goal.
The two basic programs in the Internet Convention Suite have clear functions. TCP describes how applications establish corresponding channels on the framework.
IP characterizes how to process and package each package to ensure that the correct target is reached. Each portal PC on the system checks the IP address to find out where to forward the message.
The subnet veil tells the PC or other system gadgets which part of the IP address to use to talk to the system and which part to use for voice (on different PCs).
Network address translator (NAT) is the virtualization of Internet protocol addresses. NAT can improve security and reduce the number of IPs that tend to be associated with demand.
Table of Contents
The general conventions of TCP / IP include the following:
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) handles the correspondence between Web servers and Internet browsers.
HTTPS (Secure HTTP) handles secure communication between the Web server and the Internet browser.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) handles file transfer between PCs.
How TCP / IP works
TCP / IP utilizes a client-server model of communication in which another PC (server) in the system provides help (such as sending pages) to a client or machine (client).
The stateless open game plan, the goal is to continue to use them.
In any case, the vehicle floor itself is stateful. It sends an isolated message, and its affiliation will remain established until all backpacks in the objective are acquired and rearranged.
The TCP / IP model is not quite the same as the seven-layer open framework interconnection (OSI) association model. The OSI reference model describes how to move applications on the framework.
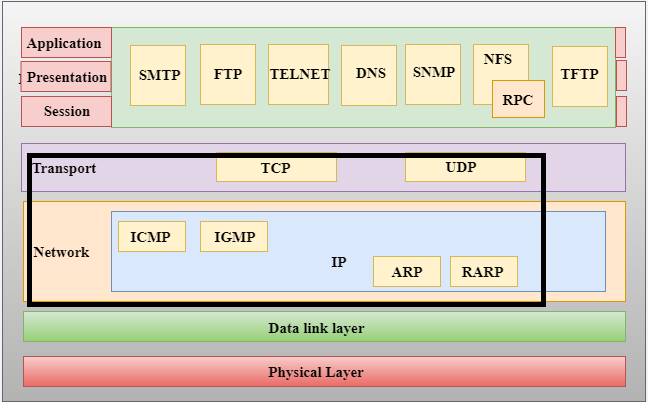
TCP IP model layer
The usefulness of TCP / IP is divided into four layers, and each layer contains explicit conventions:
The application layer provides standardized information transactions for applications. Its conventions include HTTP, FTP, Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). At the application layer, the payload is real application information.
The vehicle layer is responsible for keeping the start frame complete. TCP handles switching and provides flow control, multiplexing, and stable quality. The vehicle shows the connection of TCP and User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and for clear purposes, this convention is currently used instead of the TCP IP model.
The framework layer (also known as the Web layer) supervises the programming package and interfaces with the free framework to constrain the development of the programming package in the association. The framework layer shows IP and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), which are used for outdated disclosure.
The physical layer, also known as the system interface layer or information connection layer, consists of conventions that only function in the connection, that is, the system that connects the hub or the hub of the system. The conventions in this minimum layer include Neighbor Ethernet (LAN) and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
The meaning of TCP / IP
TCP / IP is non-proprietary and therefore not subject to any single organization. In this way, the Internet protocol suite can be adjusted without problems. So, it applies to every working frame, so it can be used with other frames.
TCP / IP is very adaptable, and as a routable protocol, you can decide on the most skilled method of going through the system. It is usually used in current Web projects.
Historical background of TCP IP Model
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the US Department of Defense Exploration Department developed the TCP / IP model for ARPANET in the 1970s.
The Internet Engineering Task Force is currently maintaining the TCP / IP model and its related conventions.
TCP / IP and OSI model
TCP / IP and OSI are the most widely used communication organization conventions. The difference in principle is that OSI is a reasonable model, not for all intents and purposes for communication. Or, it characterizes how applications are transmitted on the system.
The TCP / IP conventions extend the principles of creating networks, and the OSI model gives rules about how to complete communications. Therefore, TCP / IP is an increasingly powerful model.
The TCP / IP and OSI models have similarities and contrasts.
These are the seven layers of the OSI model:
Application layer 7 When the client needs to understand messages, move records, or participate in other system-related exercises, the client (program or person) can communicate with the application or system.
The sixth layer, the introduction layer, decrypts or arranges information for the application layer according to the semantics or grammar confirmed by the application.
The conference layer 5 was established to promote and end the discussions between applications.
The fourth layer (vehicle layer) processes the movement information on the system and provides error checking components and information flow controls.
The third layer, the system layer, moves the information into and into different systems.
The second layer, the information connection layer, deals with problems that occur due to bit transmission errors.
Layer 1, the physical layer, uses electrical, mechanical, or program interfaces to transmit information.
The upper layers of the TCP / IP model and the OSI model are both application layers. Although this layer plays a similar role in each model, these allocations may fluctuate based on the information that everyone gets.
Represented TCP / IP and OSI models
Although they will do so in various ways and in various ways, they will achieve their goals no matter what.
The similarities between the TCP / IP model and the OSI model include the following:
- They are all legal models.
- This are the characteristics of organizational meters.
- They divided the corresponding process of the system into several layers.
- This provide a structure for manufacturing and implementing scales and gadgets.
- They enable a producer to manufacture gadgets and system parts that can exist together and use them with gadgets and segments made by different manufacturers.
The comparison between the TCP / IP model and the OSI model includes the following:
- TCP / IP uses only one layer (application) to characterize the functions of the upper layer, while the OSI model uses three layers (application, presentation, and conference).
- The TCP / IP model uses one layer (interface) to characterize the functions of the base layer, while OSI uses two layers (physical layer and information connection).
- The TCP / IP model uses the Web layer to characterize steering instruments and conventions, while OSI uses the system layer.
- The size of the TCP / IP header is 20 bytes, while the size of the OSI header is 5 bytes.
- The TCP / IP model is a conventional specification, although the OSI model is a non-exclusive model, depending on the function of each layer.
- TCP / IP uses a unified method, while OSI uses a vertical method.
In the TCP / IP suite, the convention is first added, and then the model is created. In OSI, the model is first grown, and then the convention is created in each layer.
TCP / IP establishes associations between various PCs, while the OSI model standardizes switches, switches, motherboards, and other devices.
Employment of TCP / IP
It refines basic conventions or strategies for communicating at each layer as data passes.
- Advantages and disadvantages of TCP / IP
- The benefits of using the TCP / IP model include:
- Establish associations between various PCs;
What are the 4 TCP IP layers?
The four layers of the original TCP / IP model are the application layer, transport layer, Internet layer, and network access layer.
What is the difference between TCP and TCP IP?
So, the difference is that TCP is responsible for data transmission of data packets. Then, IP is responsible for logical addressing. For more information on this topic, please read Understanding TCP / IP.
What is meant by TCP IP?
Through, TCP / IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. Which is a set of network protocols that allows two or more computers to communicate? The Defense Data Network of the Ministry of Defense has developed TCP / IP.